Direct Air Capture Technology
What is Direct Air Capture?
Direct Air Capture (DAC) is an important climate solution that removes excess carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the atmosphere. Science and industry agree that DAC projects are an urgent necessity to remove excess CO2 from the atmosphere. This will help to prevent worsening extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods, in the long term.
Climeworks’ Technology
Climeworks’ technology includes modular CO2 collectors that can be stacked to build facilities at any capacity and are powered solely by renewable and waste energy. The collectors remove CO2 from the air: First, air is drawn into the collector, where the CO2 is captured on the surface of a highly-selective filter material in a process called "adsorption." Next, when the filter is full of CO2, the collector is closed and the material is heated to about 210°F to release the CO2 in a process called "desorption." The CO2 is collected in high purity and concentration and the process repeats.
Project Cypress will deploy proven DAC technology from two companies: Climeworks and Heirloom.
Heirloom’s Technology
Heirloom’s technology rapidly accelerates the natural processes that enable limestone to adsorb CO2 from the air from a time span of years down to days. Limestone is the world’s most abundant material and is used in medicine, cosmetics, and food production among other uses. In this process, the limestone is heated in a renewable-energy powered electric kiln to remove the CO2 which is then permanently stored. The mineral is laid on vertically stacked trays - where the limestone acts like a sponge, pulling CO2 from the atmosphere. This process is repeated over again in a loop to continuously sponge CO2 from the atmosphere.
Is DAC the same as Point Source CO2 Capture?
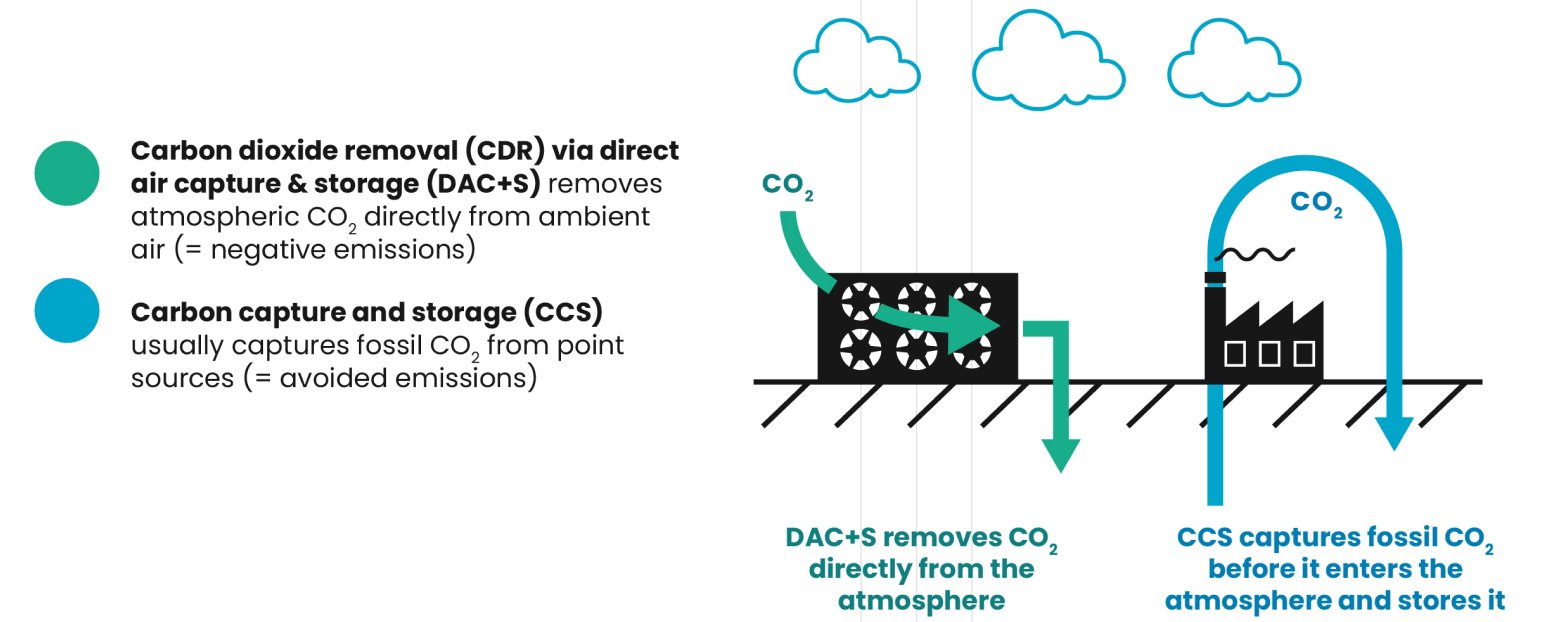
Unlike carbon capture, which is situated at a point source, like a factory or power plant, and prevents emissions from entering the atmosphere, DAC removes CO2 that has already been emitted into the atmosphere directly from the air. None of the CO2 Project Cypress removes will be used to enable fossil fuel extraction through methods like enhanced oil recovery.
DAC is carbon negative while point source CO2 capture achieves carbon neutrality at best.
Where does CO2 go once it’s been captured?
Once captured, the CO2 is stored underground in cooperation with an experienced storage partner. Storing CO2 underground has been an industry practice for more than four decades and is well-understood and safe. Wells used to inject CO2 into the ground are Class VI wells, built with strong materials that are highly tolerant to CO2 and built to prevent leaks and corrosion. For this project, CO2 will be stored about 7,000 feet underground.